Ultrasound (Sonography)
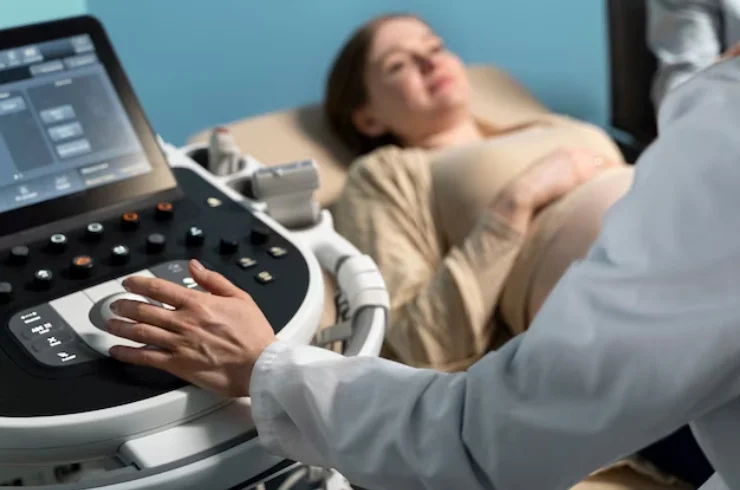
Ultrasound, also known as sonography, is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the internal structures of the body. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, ultrasound does not involve ionizing radiation, making it a safer imaging option for patients, especially pregnant women and children.
Ultrasound works by emitting sound waves from a small probe called a transducer, which is placed on the skin over the area of interest. These sound waves travel through the body and bounce off tissues, organs, and other structures. The returning echoes are captured by the transducer and converted into real-time images that can be displayed on a monitor.
Ultrasound is commonly used for imaging soft tissues, such as muscles, organs (e.g., liver, kidneys, heart), blood vessels, and the fetus during pregnancy.
It is particularly valuable for visualizing organs and structures that are difficult to assess using other imaging techniques. For example, ultrasound is the gold standard for assessing the health and development of the fetus, monitoring the growth of tumors or cysts, and evaluating the heart’s function.
Some of the common applications of ultrasound include:
- Obstetrics and Gynecology: Monitoring fetal development, assessing the health of the ovaries and uterus, and guiding procedures like amniocentesis.
- Cardiology: Echocardiograms to assess heart function and detect issues like valve problems or fluid accumulation around the heart.
- Abdominal Imaging: Evaluating the liver, gallbladder, kidneys, and pancreas for abnormalities such as tumors, stones, or cysts.
- Musculoskeletal Imaging: Assessing muscles, tendons, and joints for injuries or conditions like tendonitis.
Ultrasound is widely appreciated for its ability to provide real-time, dynamic images with minimal risk, making it an invaluable tool in both diagnostic and therapeutic settings. However, its use may be limited in some areas where high resolution is required, such as for imaging dense tissues like bones.



