- +91-9171082108
- +91-9171083108
- admin@sathamanamclinics.com
- Hyderabad, India
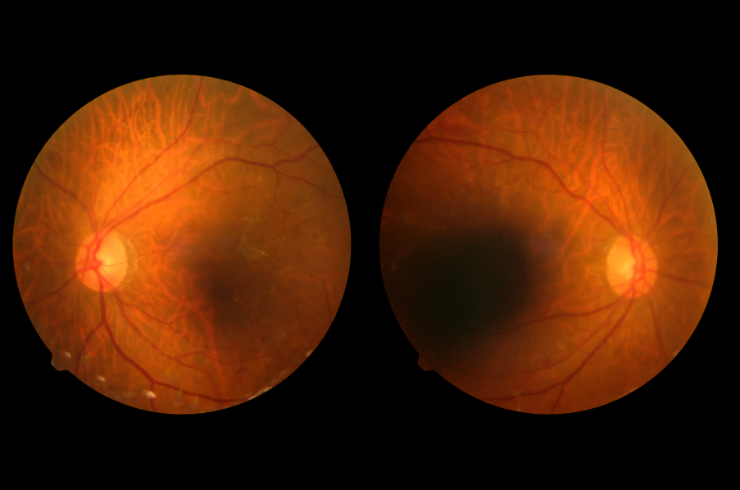
Diabetic Retinopathy: Understanding, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes-related eye condition that affects the blood vessels of the retina, which can lead to vision loss if left untreated. It is one of the leading causes of blindness in adults, making knowledge about its risk factors, symptoms, and management essential for individuals with diabetes.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy occurs when high blood sugar levels damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. Over time, this damage can lead to leakage of fluid and blood, causing swelling and vision problems. It can also result in the growth of new, abnormal blood vessels that can further damage your eyesight.
Types of Diabetic Retinopathy
Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR): This is an early stage of diabetic retinopathy characterized by changes in the retina’s blood vessels, including microaneurysms and leakage of fluid and blood. Vision may not yet be significantly affected.
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR): In this advanced stage, new blood vessels begin to grow along the retina and into the vitreous (the gel-like substance that fills the eye). These new vessels can be fragile and bleed, leading to more severe vision impairment.
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
Individuals may not notice symptoms in the early stages of diabetic retinopathy. However, as the condition progresses, symptoms may include:
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy:
Diagnosis
Diabetic retinopathy is typically diagnosed through a comprehensive eye exam, which may include:
Treatment Options
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy depends on the severity of the condition:
1. Monitoring
In the early stages (NPDR), monitoring the condition closely may be sufficient. Regular eye exams are essential to track progression.
2. Laser Treatment
For more advanced stages (especially PDR), laser treatment may be recommended:
3. Injections
Medications may be injected into the eye to:
4. Vitrectomy
In cases of severe retinopathy with vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment, a vitrectomy may be performed. This surgery removes the vitreous gel along with any blood and scar tissue.
Preventive Measures
Preventing diabetic retinopathy involves managing diabetes effectively:
Conclusion
Diabetic retinopathy is a serious condition that can lead to vision loss if not managed properly. Understanding its risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for individuals living with diabetes. Regular eye exams and proactive management of diabetes are key to preventing this complication.
If you or a loved one is concerned about diabetic retinopathy or needs to schedule an eye examination, contact Sathamanam Clinics for expert care and guidance. Our team of healthcare professionals is dedicated to providing comprehensive support for diabetes management and eye health.
Empowering your health journey with personalized care, advanced treatments, and compassionate support at Sathamanam Clinics. Your well-being is our priority!
WhatsApp us